Non-contact forces are forces that act between two objects without any physical contact between them.
Non-contact forces include gravity, electromagnetism, the strong force, and electromagnetic radiation (e.g. radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays).
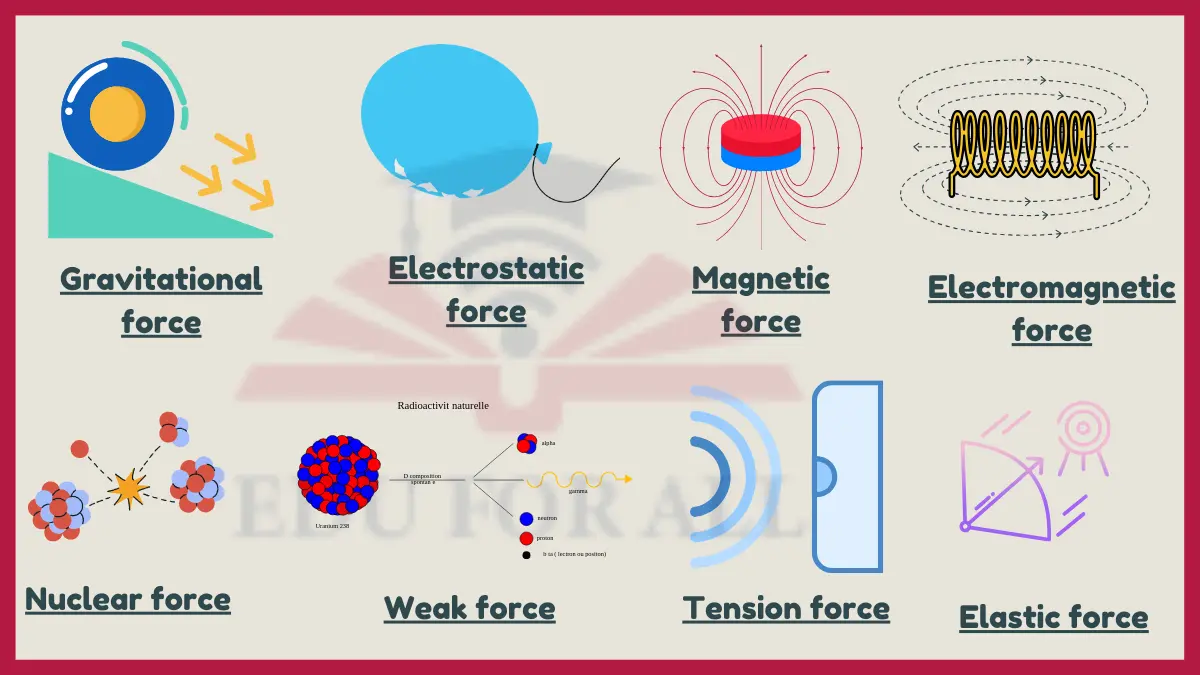
Examples of Non Contact Forces
Here are 14 examples of non contact forces in daily life:
1. Gravitational force
The gravitational force is one of the most common examples of non-contact force. It is responsible for holding the planets in their orbits around the sun. The gravitational force also acts between all objects with mass, including us.
Gravitational force is mediated by the exchange of gravitons, which are massless particles that can travel through space at the speed of light. This means that the gravitational force between two objects can act even if they are not touching.
2. Electrostatic force
Electrostatic forces can act over distances between charged objects without physical contact. The electrostatic force is a force of attraction or repulsion between electrically charged objects.
The electrostatic force is responsible for the attraction between a balloon and your hair after you rub it on your head, and it also responsible for lightning.
The electrostatic force is mediated by the exchange of photons, which are also massless particles that can travel through space at the speed of light. This means that the electrostatic force between two electrically charged objects can act even if they are not touching.
3. Magnetic force
Magnetic forces can attract or repel objects from a distance without contact. The magnetic force is a force of attraction or repulsion between magnetic objects.
The magnetic force is responsible for the attraction between a magnet and a piece of iron, and it is also responsible for the Earth’s magnetic field.
The magnetic force is mediated by the exchange of virtual photons, which are particles that are created and destroyed in pairs. Virtual photons can travel through space at the speed of light, even though they cannot exist for long periods of time.
This means that the magnetic force between two magnetic objects can act even if they are not touching.
4. Electromagnetic force
Electromagnetic forces can interact over distances without physical contact. The electromagnetic force is a fundamental force that is responsible for all electrical and magnetic interactions.
The electromagnetic force is responsible for the attraction between electrons and protons in atoms, and it is also responsible for the propagation of light.
The electromagnetic force is a combination of the electrostatic force and the magnetic force. It is mediated by the exchange of photons, just like the electrostatic force.
This means that the electromagnetic force between two objects can act even if they are not touching.
5. Nuclear force
The nuclear force binds nucleons together within the nucleus without contact. The nuclear force is a force that binds together the protons and neutrons in the nuclei of atoms.
The nuclear force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, and it is responsible for the stability of atoms and the release of energy in nuclear reactions.
The nuclear force is mediated by the exchange of gluons, which are particles that bind quarks together to form protons and neutrons. Gluons cannot travel through space on their own, but they can be exchanged between quarks inside of protons and neutrons.
This means that the nuclear force can only act between objects that are very close together, such as the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
6. Weak force
The weak force causes radioactive decay through action at a distance without contacting the decaying nucleus. The weak force is a fundamental force that is responsible for certain types of radioactive decay, such as beta decay. The weak force is also responsible for the interaction between neutrinos and matter.
The weak force is mediated by the exchange of W and Z bosons, which are massive particles that can travel through space at the speed of light. However, the W and Z bosons have a very short lifetime, so the weak force can only act over very short distances.
This is why the weak force is responsible for certain types of radioactive decay, where particles are emitted from the nucleus of an atom.
9. Elastic force
The elastic force is caused by the stretching or compression of a spring or other elastic object. When a spring is stretched, the molecules inside the spring are pulled further apart. When a spring is compressed, the molecules inside the spring are pushed closer together.
In either case, the molecules inside the spring are trying to return to their original positions. This is why the elastic force always acts in the opposite direction of the displacement of the spring.
10. Radio waves
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that can travel through space at the speed of light. Radio waves are produced by the oscillation of electric and magnetic fields.
This oscillation can be caused by a variety of sources, such as lightning, radio transmitters, and even cosmic rays.
Radio waves can travel through space without any physical contact with the objects they interact with. This is why radio waves can be used to transmit information over long distances.
11. Microwave radiation
Microwave radiation is another example of non contact forces. Microwave radiation is produced by the oscillation of electric and magnetic fields. This oscillation can be caused by a variety of sources, such as microwave ovens, masers, and even pulsars.
Microwave radiation can travel through space without any physical contact with the objects it interacts with. This is why microwave radiation can be used to heat food and cook meals.
12. Infrared radiation
Infrared radiation is another example of non contact forces. Infrared radiation is produced by the vibration of atoms and molecules. This vibration can be caused by a variety of sources, such as hot objects, blackbody radiation, and even lasers.
Infrared radiation can travel through space without any physical contact with the objects it interacts with. This is why infrared radiation can be used to see in the dark and to keep us warm.
13. Ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet radiation is a non-contact forces that is produced by the transition of electrons between energy levels in atoms and molecules. This transition can be caused by a variety of sources, such as the Sun, fluorescent lights, and even welding arcs.
Ultraviolet radiation can travel through space without any physical contact with the objects it interacts with. This is why ultraviolet radiation can be used to tan skin and to sterilize equipment.
14. X-rays
X-rays are non-contact forces that interact with matter by causing ionization. X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation that can be used to see through the skin and bones.
They can interact with matter without physically contacting it. This is because X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, and electromagnetic radiation can travel through space without any physical contact with the objects it interacts with.

