Some common examples of fungi are mushrooms, molds, yeasts, truffles, and shelf fungi. Button mushrooms and portobello mushrooms are fungi frequently used for cooking. Penicillium mold produces the lifesaving antibiotic penicillin. Baker’s yeast helps bread rise.
The pungent black truffle is a culinary delicacy. Shelf fungi sprout from trees as hard, plant-like growths. Additionally, the fungus responsible for athlete’s foot causes flaky skin. Mushrooms form visible fruiting bodies, while molds and yeasts consist of microscopic filaments and single cells respectively. Fungi obtain nutrients by secreting enzymes onto their food source and absorbing the digested compounds.
Examples of Fungi
Here are 10 examples of fungi:
1. Button Mushroom
Scientific Name: Agaricus bisporus
The button mushroom is a commonly eaten mushroom. It has a white stem and brownish cap. Button mushrooms are grown commercially indoors in specially prepared compost.

Experiment: You can find button mushrooms at the grocery store or farmer’s market. They are commonly sold fresh or canned.
2. Baker’s Yeast
Scientific Name: Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Baker’s yeast is a single-celled fungus used to leaven bread. It feeds on sugars and converts them into carbon dioxide and alcohol through fermentation. Baker’s yeast causes dough to rise, creating air pockets that result in light, fluffy baked goods.

You can find baker’s yeast in the baking aisle at the grocery store. Check dry active yeast or fresh cakes of yeast.
3. Penicillium
Scientific Name: Penicillium spp.
Penicillium fungi produce the antibiotic penicillin, which fights bacterial infections. There are hundreds of Penicillium mold species which often grow as fuzzy blue-green patches on old bread, fruit, or damp walls.
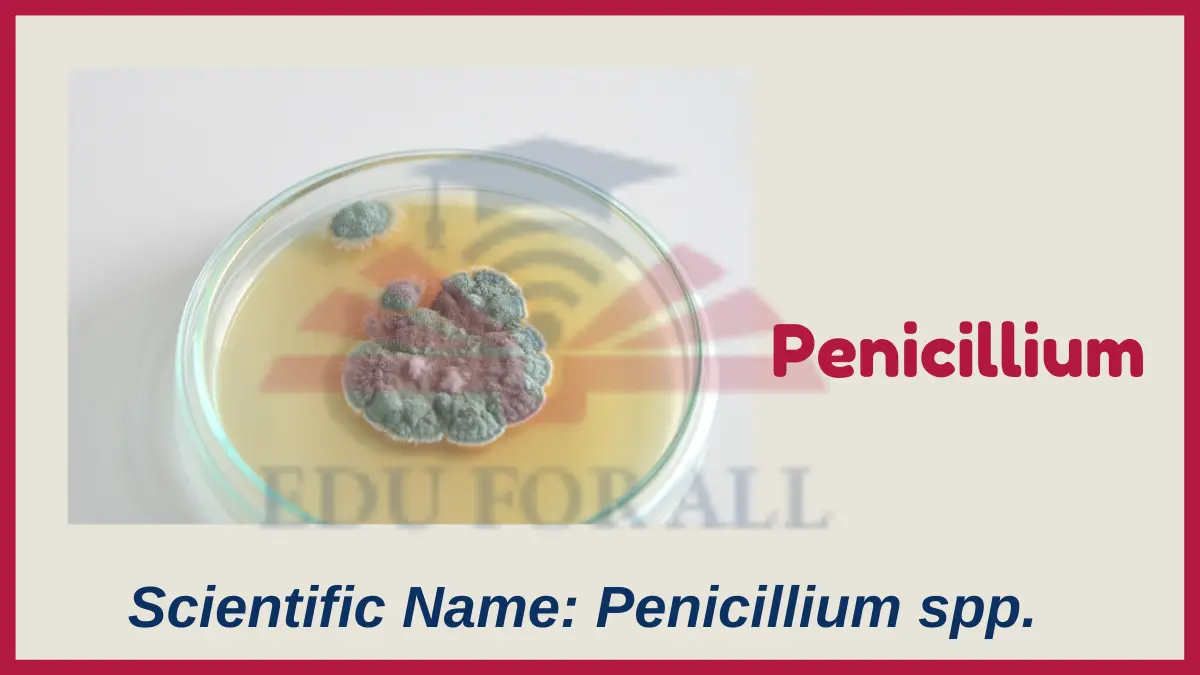
You can find penicillium molds growing on old bread, fruit peels, cheese, or damp areas of a bathroom.
4. Athlete’s Foot Fungus
Scientific Name: Trichophyton rubrum
This fungus lives on the skin and causes itchy, peeling areas between the toes or blisters on the feet. It spreads through contact in damp public areas like gyms, pools, and showers.
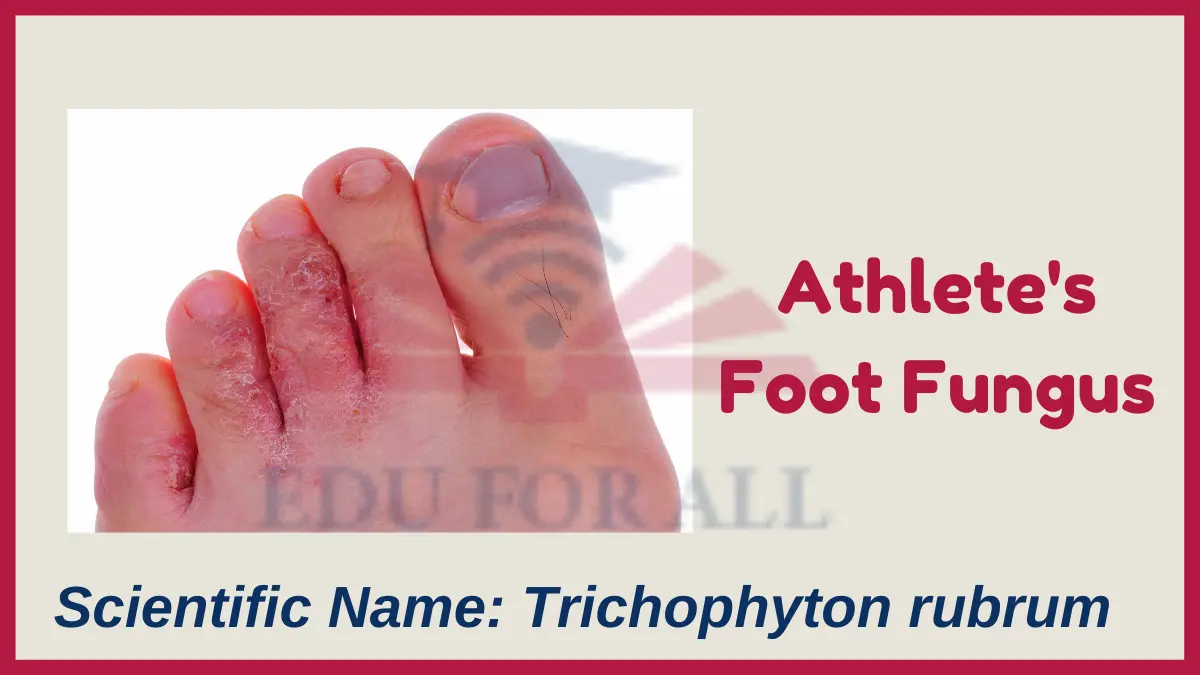
You can find athlete’s foot fungus by examining between the toes or on the feet of someone with symptoms of scaling/peeling skin or blisters.
5. Aspergillus
Scientific Name: Aspergillus spp.
Aspergillus mold species are very common and grow on decomposing plant matter, household dust, or building materials. Most don’t cause illness but some release toxins or trigger allergic reactions.

You can find aspergillus molds on foods past their prime like stale bread, old peanuts, or decomposing produce.
6. Sac Fungus
Scientific Name: Xylaria polymorphia
This wood-decay fungus has a fruiting body shaped like a tiny club protruding from rotting logs or stumps. Its common name refers to its sac-like cups where spores develop.

You can find sac fungus growing as tiny black clubs on dead wood while walking through the forest, especially northern hardwood forests.
7. Candida
Scientific Name: Candida albicans
Candida fungi normally grow harmlessly on human skin and mucous membranes. But overgrowth causes infections like oral thrush or vaginal yeast infections, especially in immunocompromised people.
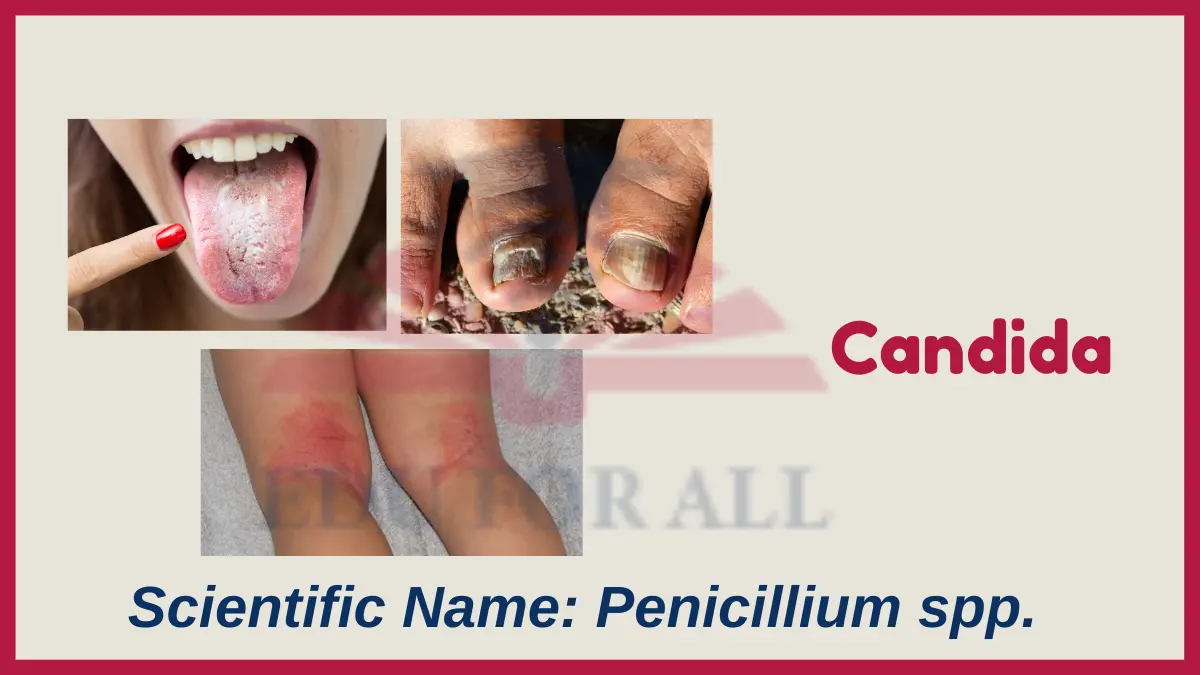
You can find candida fungi normally growing harmlessly on human mucous membranes like the mouth and digestive tract.
8. Truffles
Scientific Name: Tuber spp.
Truffles are edible fungi that develop underground near tree roots in a symbiotic relationship. They have a strong, earthy aroma and are considered a culinary delicacy.

You can find truffles at gourmet restaurants served shaved over pasta or meat. Truffle oil and salt also contain truffle pieces.
9. Shelf Fungus
Scientific Name: Fomes fomentarius
Shelf fungi grow as hard, hoof-shaped fungal plates projecting outward from the bark of dead or dying trees. They decay and consume the dead wood they grow on.

You can find shelf fungi growing as hard plates or mushrooms on dead wood like fallen trees and logs when walking outdoors.
10. Meadow Mushroom
Scientific Name: Agaricus campestris
This edible gilled mushroom has pink-colored caps and grows prolifically in grassy areas, often forming fairy rings. It is the wild variant of the cultivated button mushroom.

You can find meadow mushrooms growing in fairy rings in fields and grasslands, especially after rain. Can sometimes be found at farmers markets as well.

