The refraction of light refers to the bending of light waves when they pass from one transparent medium into another, such as from air into water. This occurs because light changes speed when moving between materials of different densities.
Some common examples of light refraction include prisms separating white light, mirrors bending image paths, and even the appearance of depth in swimming pools.
- Examples of Refraction of Light
- 1. Rainbows
- 2. Diamonds
- 3. Eyeglasses
- 4. Looking through glass or water
- 5. Fiber Optic Cable
- 6. Cameras
- 7. Microscopes
- 8. Telescopes
- 9. Looming Effect
- 10. Fluorescence
- 11. 3D Movies
- 12. Prisms
- 13. Mirages
- 14. Reading Glasses
- 15. Fish Tanks
- 16. Phone Camera Lenses
- 17. Apparent Depth In Pools
- 18. Glimmering Soap Bubbles
- 19. Heated Roadway Signs
- 20. Multicolored sports sunglasses
Examples of Refraction of Light
Here are some real world Examples of Refraction of Light:
1. Rainbows
Rainbows demonstrate refraction as sunlight enters a water droplet, slows down and bends, reflects off the inside of the droplet, and bends again as it exits into the air. This separates the sunlight into the colors of the rainbow.
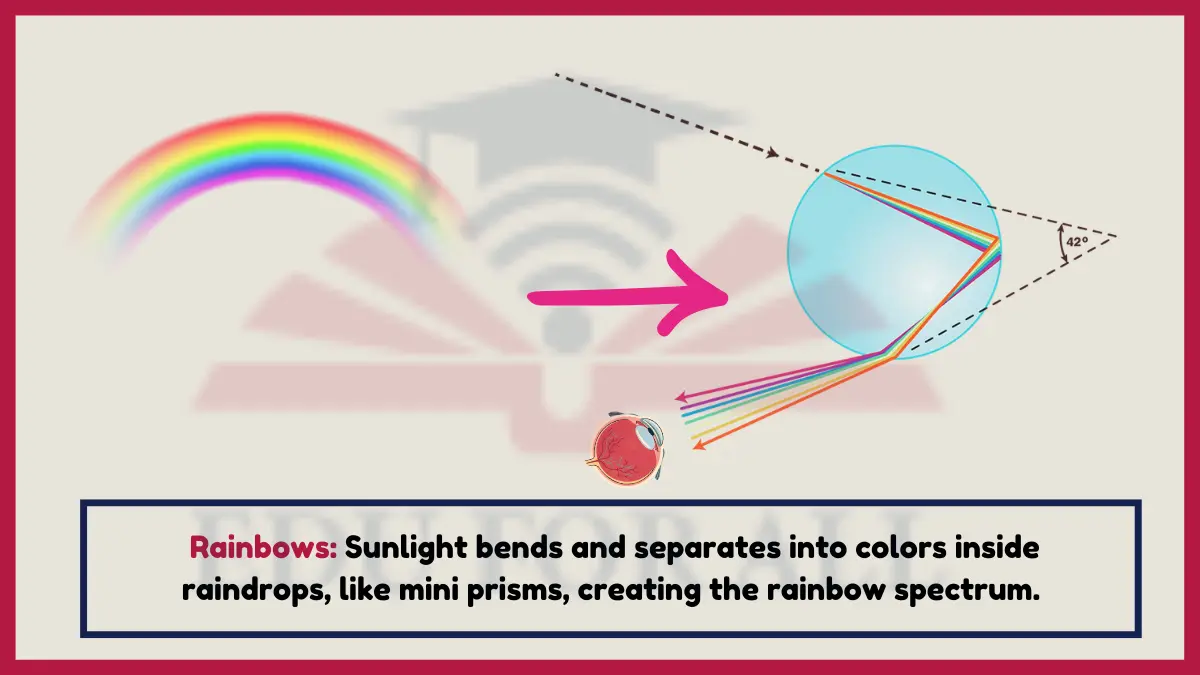
Red light refracts the least, while violet refracts the most in a rainbow.
Experiment: Spray a garden hose on a sunny day to see miniature rainbows in the mist.
2. Diamonds
Light refracts internally in diamonds, dispersing spectra that give diamonds their brilliance and fire qualities.
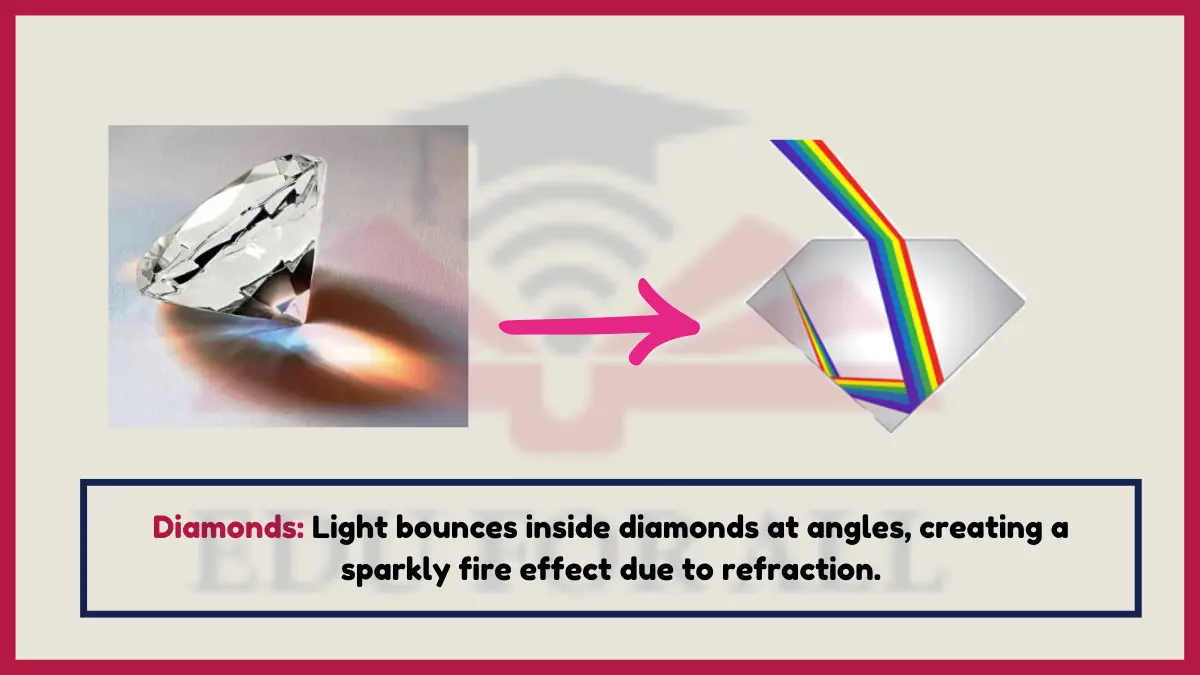
Diamonds have a very high refractive index of 2.4.
Experiment: Shine light through a real or simulated diamond to see dispersed colors.
3. Eyeglasses
Corrective lenses in glasses compensate for refractive defects in patient’s eyes to restore focus.

Eyeglass material and lens curvature is chosen based on an individual’s sight diagnosis.
Experiment: Look through different strength reading glasses to appreciate corrective refraction.
4. Looking through glass or water
When looking at objects through substances like glass, water, or a gemstone, the light bends as it passes from the air to the substance, making objects appear distorted or offset from their actual position.
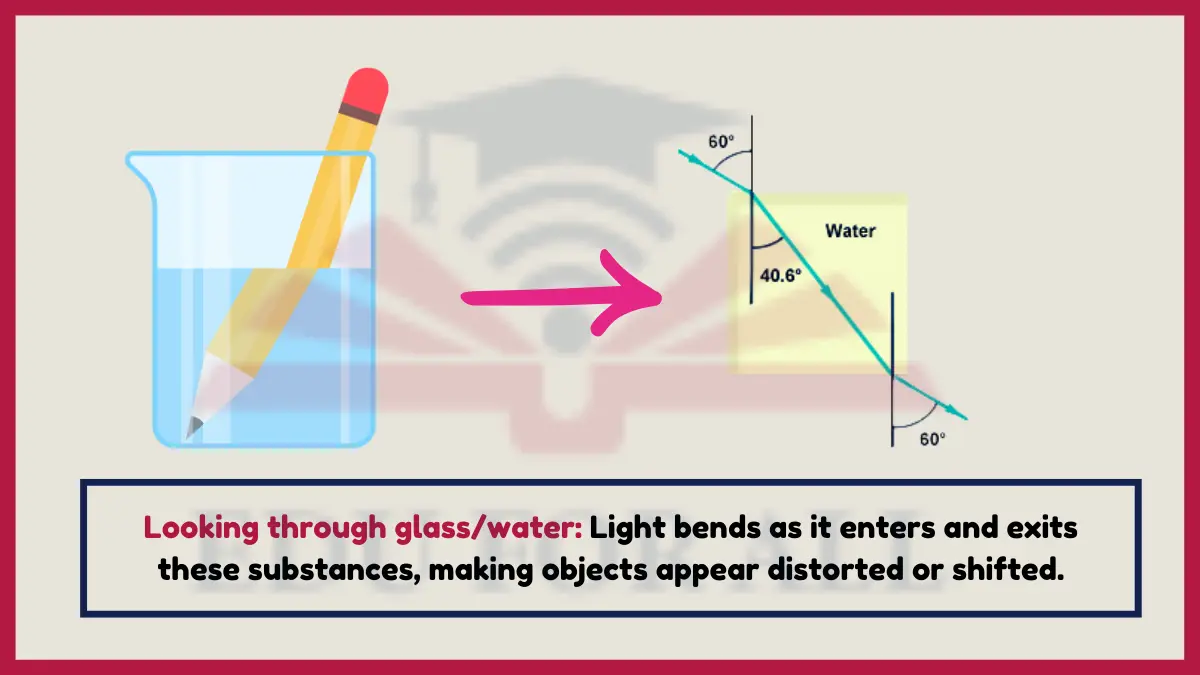
Experiment: Students can observe this refraction firsthand by placing a straight object like a pencil partially in a clear glass of water and noting the suddenly offset or “broken” appearance at the point where the image transitions from air to water.
5. Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cables contain glass or plastic fibers that rely on total internal reflection and refraction to transmit data via light signals.
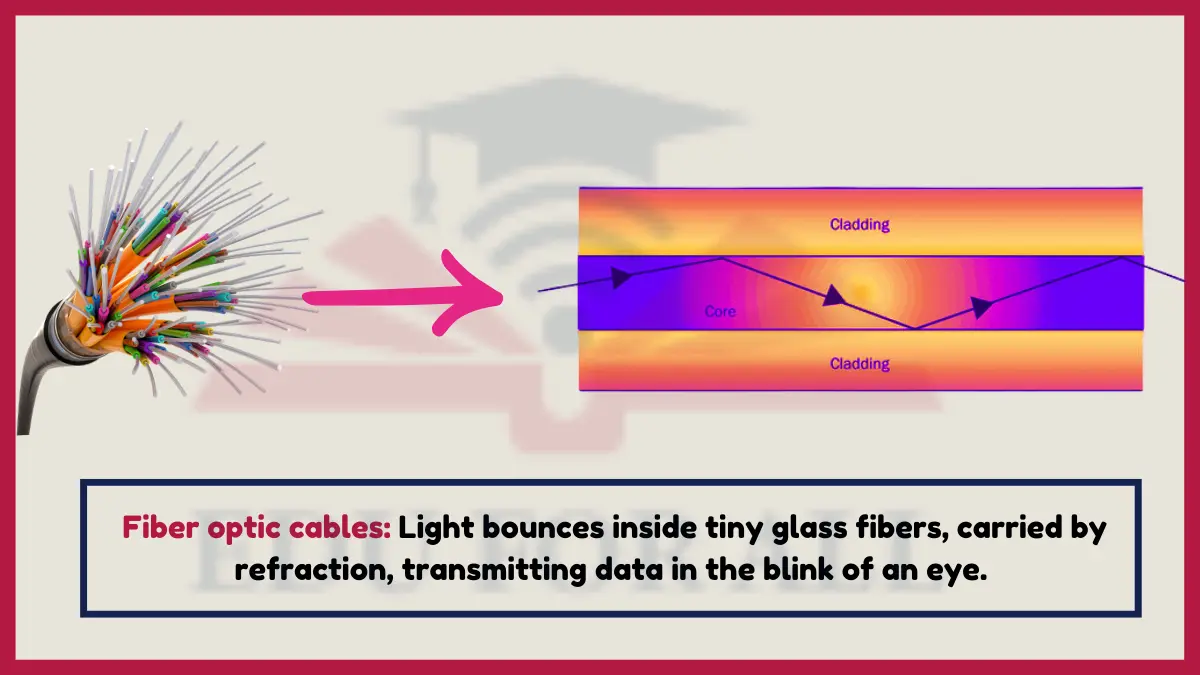
Fiber internet provides 100x faster speeds than copper cables by encoding data in refracted light beams.
6. Cameras
Camera lenses are specially shaped to converge refracted light rays sharply capturing images onto film or digital sensors.
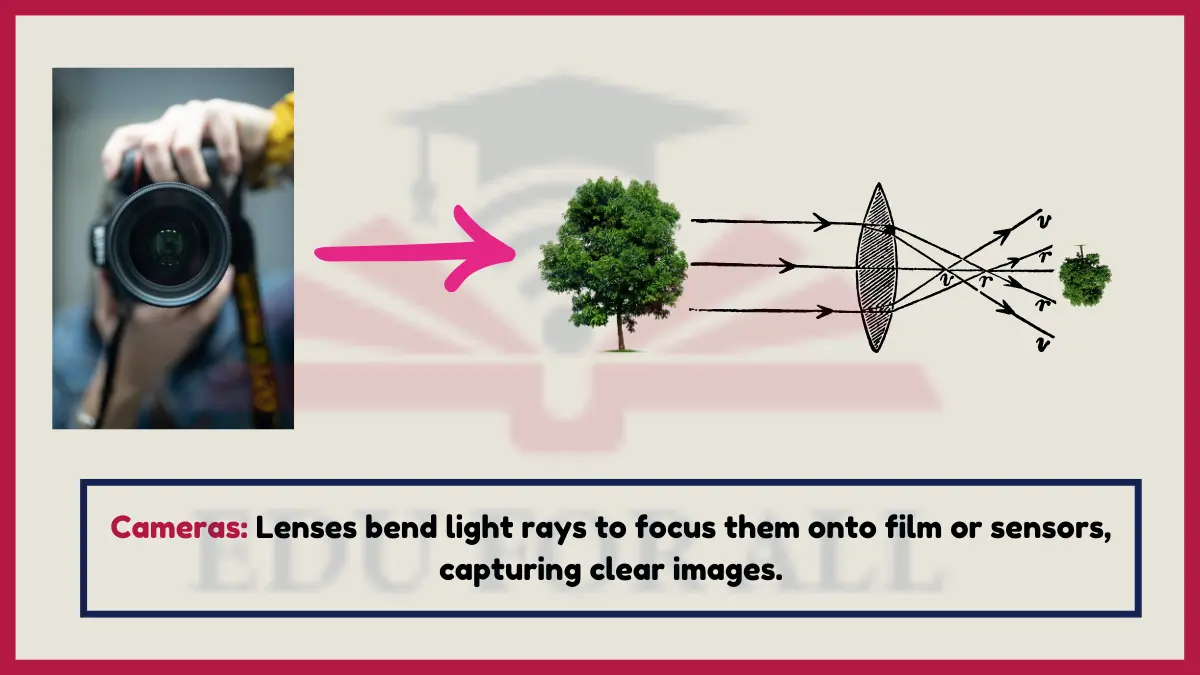
Camera apertures adjust to control the amount of refracted light entering to properly expose shots.
Experiment: Use sunlight, paper and pinholes to demonstrate how cameras capture images via refracted light inside enclosed boxes.
7. Microscopes
Multiple glass lenses magnify tiny microbe samples by bending light via precise angles of refraction to resolve microscopic details.
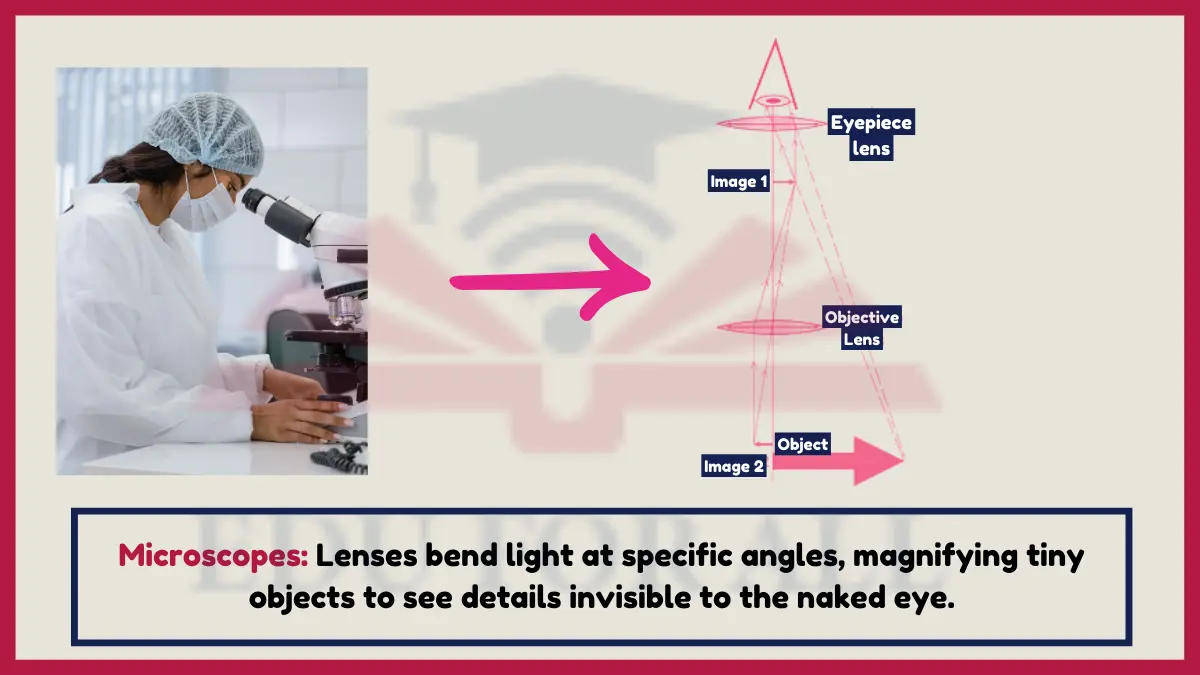
Electron microscopes focus beams with magnetic lenses, not glass optics.
Experiment: View fabric fibers under cheap plastic lens magnifiers appreciating the power of refraction to see microscopic textures.
8. Telescopes
Enormous terrestrial and orbital refracting telescopes gather the miniscule amount of light coming from distant stars and galaxies across space.
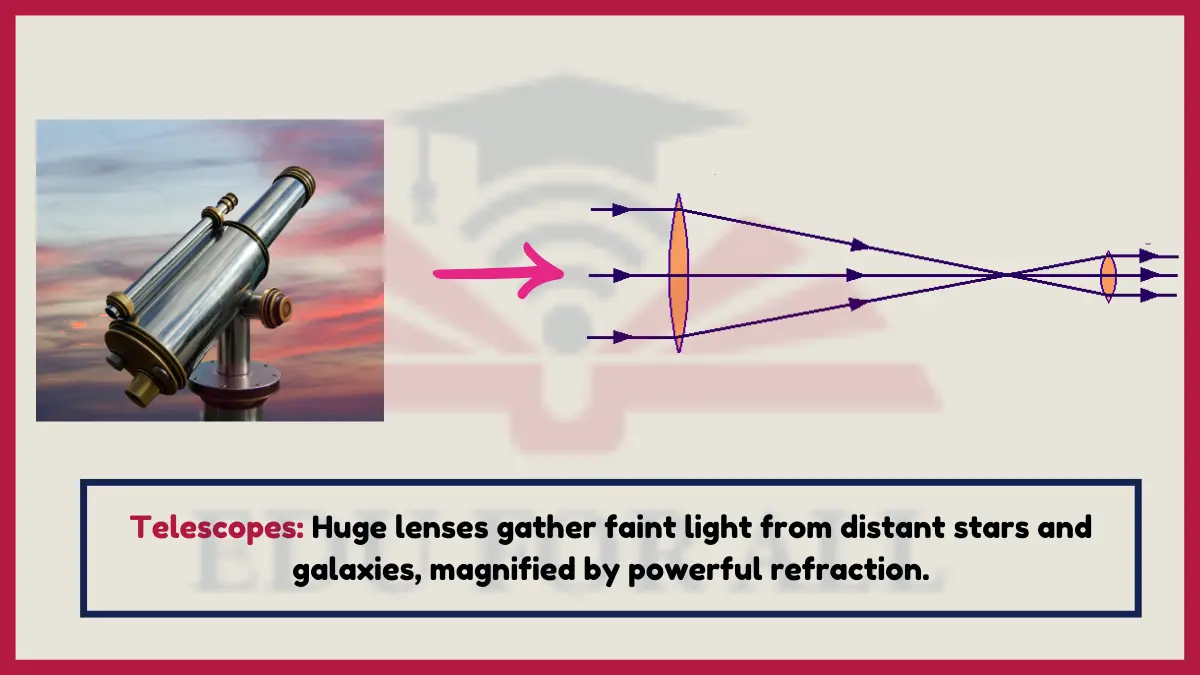
The Hubble Space Telescope orbits Earth collecting highly refracted low light from over 13 billion light years away!
Experiment: Use binoculars outside at night to see refractive magnification revealing more stars than the naked eye can discern alone.
9. Looming Effect
Light bends downward traveling through cooler air above heated asphalt or desert sand creating upside-down mirages of distant objects apparently reflected in the sky due to refraction.
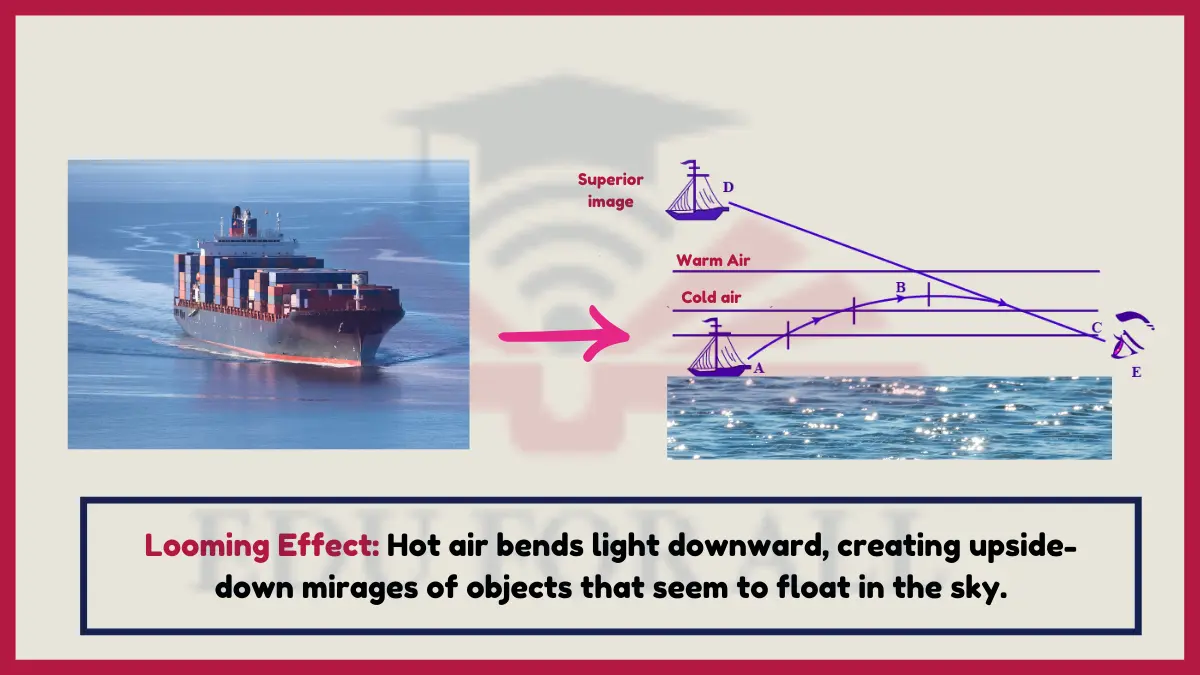
Hot road mirages result from varying air densities bending light via refraction.
Experiment: Observe upside down inferior mirages of objects across hot parking lots on sunny summer days.
10. Fluorescence
Ultraviolet light excites fluorescent substance electrons that emit refracted visible light photons creating a glow effect under black lights.
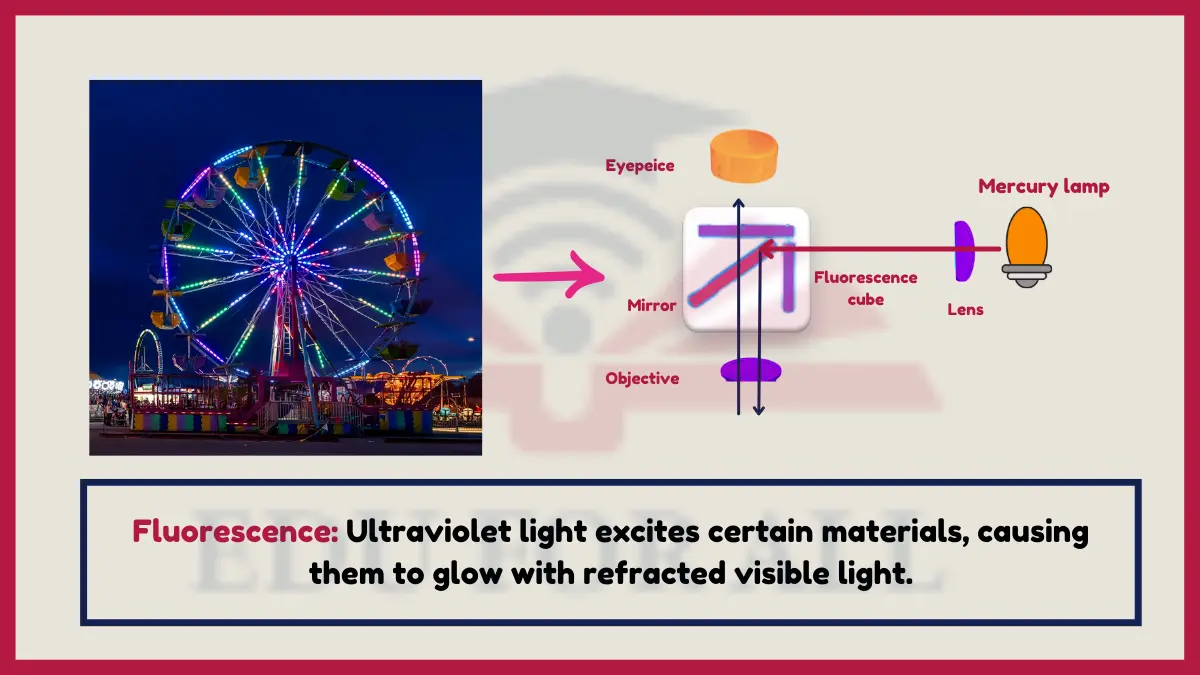
Scorpions glow blue-green under UV light due to fluorescence compounds in their exoskeletons.
Experiment: Shine UV black lights on highlighters, laundry detergent, neon art paint and your own white clothes to see refractive fluorescence.
11. 3D Movies
Special glasses filter offset images to each eye relying on the brain’s ability to recombine and interpret their differences as a single 3D scene using refractive depth cues

3D only works because your eyes (and cameras) see images from two slightly different horizontal angles due to the natural distance between them.
Experiment: Hold your finger up close to your face and alternate closing each eye to appreciate the horizontal distance and angle shifts creating your natural refractive 3D vision.
12. Prisms
When white light enters an angled prism, refraction causes the different wavelengths corresponding to each color to bend by different amounts, resulting in visible color dispersion and separation
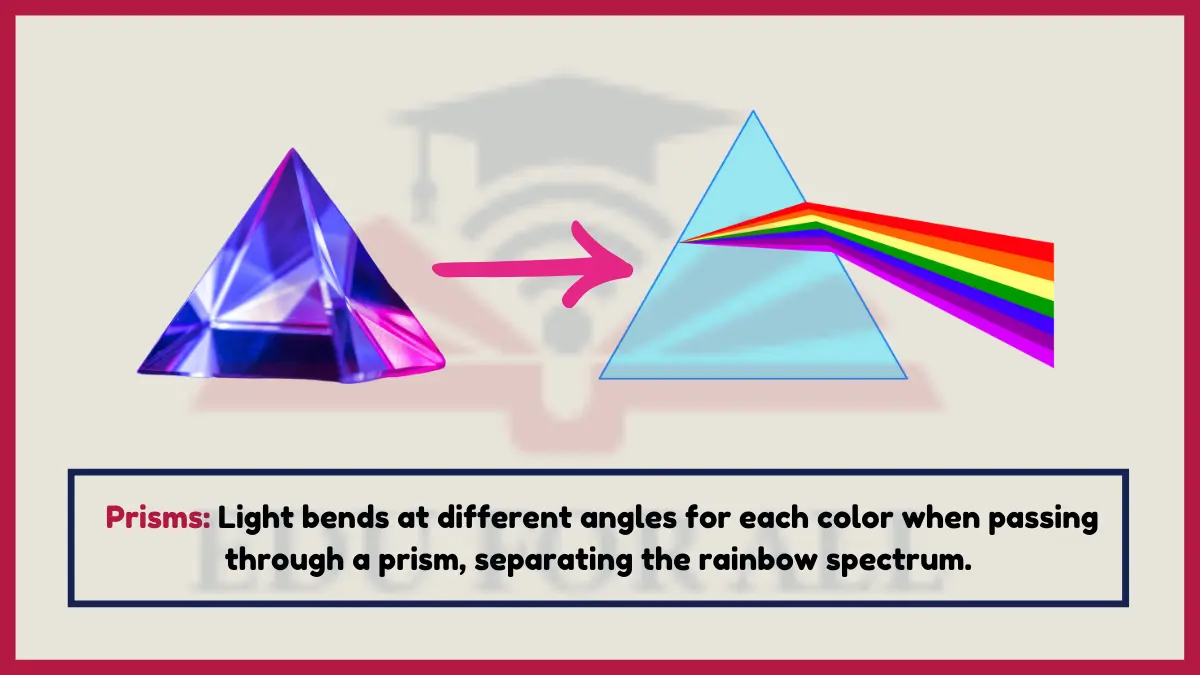
Violet light waves have shorter wavelengths than red light waves.
Experiment: Shine sunlight or an LED flashlight through prisms or crystal pendants to create miniature rainbows on walls from refractive dispersion.
13. Mirages
Rising heat from desert sand or roads creates varying air density that bends and inverts images of distant objects through differential refraction.
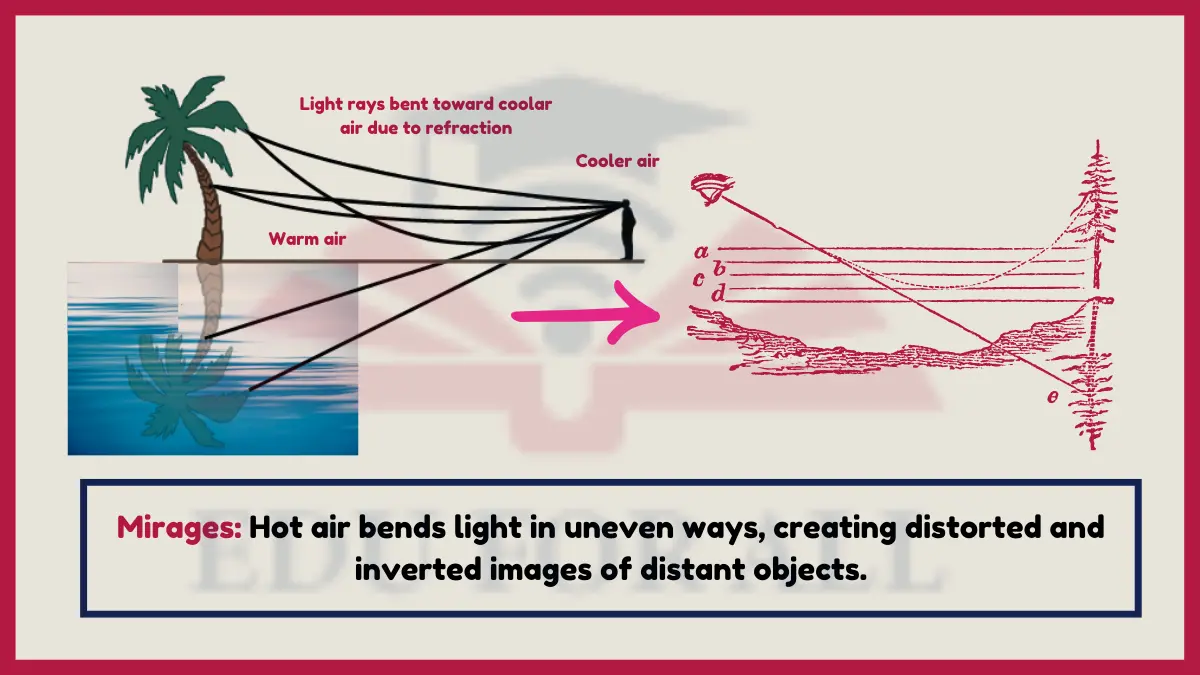
Mirages demonstrate curved light path bending between warm and cold air pockets with distinct refractive indexes.
Experiment: Notice distorted rippling reflections behind hot cooking and grilling surfaces as rising air densities unevenly refract background scene light.
14. Reading Glasses
Corrective lenses refract light differently to improve focus for those struggling to see small print.
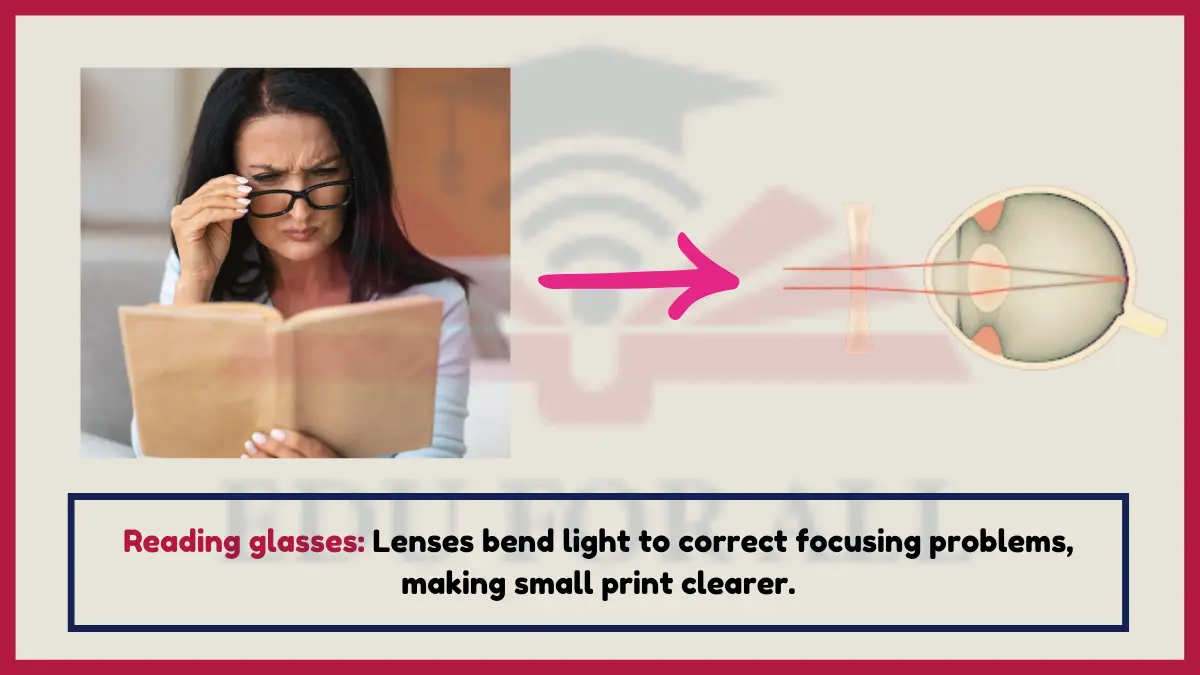
The strength of prescription lenses needed correlates to severity of refractive vision defects. Experiment: Look through drugstore reading glasses to appreciate corrective refraction.
15. Fish Tanks
Partially submerged objects behind fish tanks appear disjointed due to the water-to-air boundary refracting light beams at sharply differing angles.

Fact: Light bends towards the perpendicular when entering water, making objects seem higher than their true position.
Experiment: Place pencils in a clear water-filled vase to observe distorted heights via refractive bending at the air-water interface.
16. Phone Camera Lenses
Smartphone cameras use high-precision ground lenses to capture focused light images by bending rays to converge perfectly onto electronic image sensors.
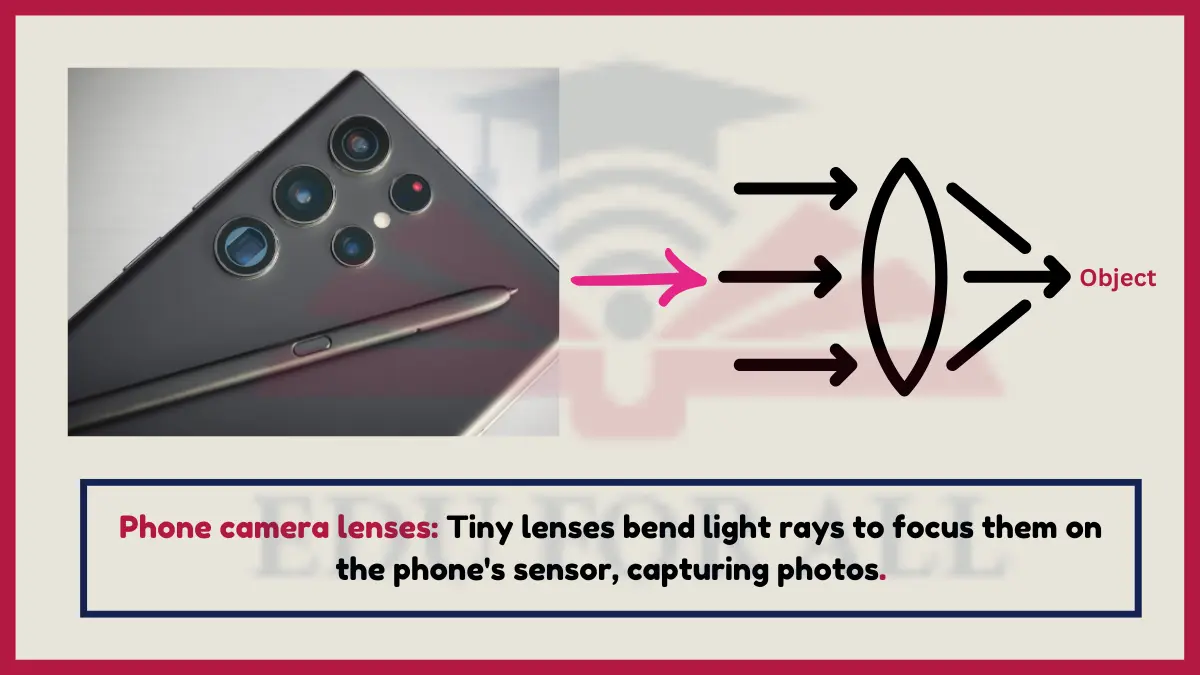
Phone cameras adjust internal optics to refract varying amounts of light for proper exposures under different brightness conditions.
Experiment: Examine the external lens hardware built into cell phone cameras to consider the refractive technology enabling photography anywhere, anytime.
17. Apparent Depth In Pools
Light reflects and refracts differently off pool walls versus the water surface itself, making bottom patterns seem raised closer than actual depth due to exaggerated angular refractive distortion.
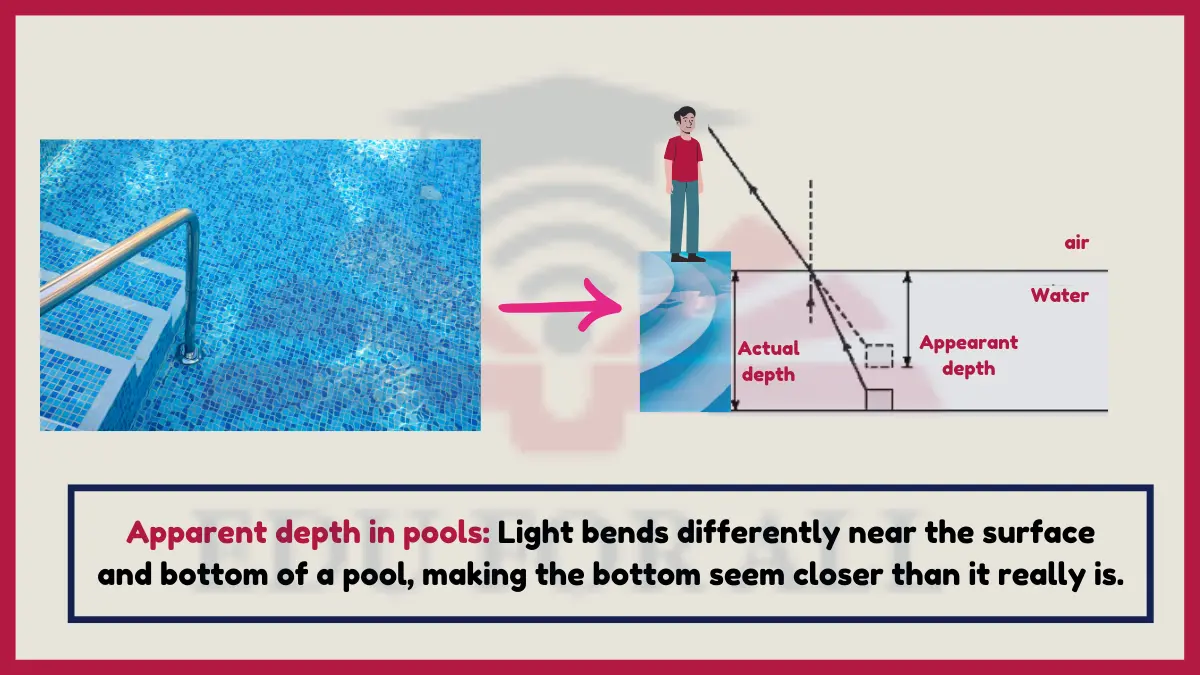
Refraction causes optical pool illusions that must be considered to avoid dangerously misjudging dive distances.
Experiment: Compare pool depths via cues like foam noodle lengths, then enter wearing goggles to experience refractive boundary transitions more safely.
18. Glimmering Soap Bubbles
Light traversing soap film interfaces falling on surrounding water refracts into flickering rainbow bands around bubbles until they pop from optical interference.

Shimmering bubble luminance results from light interference with reflections off ultra-thin separating soap and air interfaces acting like optical filters.
Experiment: Blow iridescent bubbles using dish soap formulas and observe refractive rainbow effects firsthand when sunshine hits floating or fallen soap spheres.
19. Heated Roadway Signs
Convex road safety mirror lenses use controlled refraction to widen hazardous hidden oncoming traffic viewing angles, improving intersection awareness by collecting, magnifying and directing light sources over blind spots.
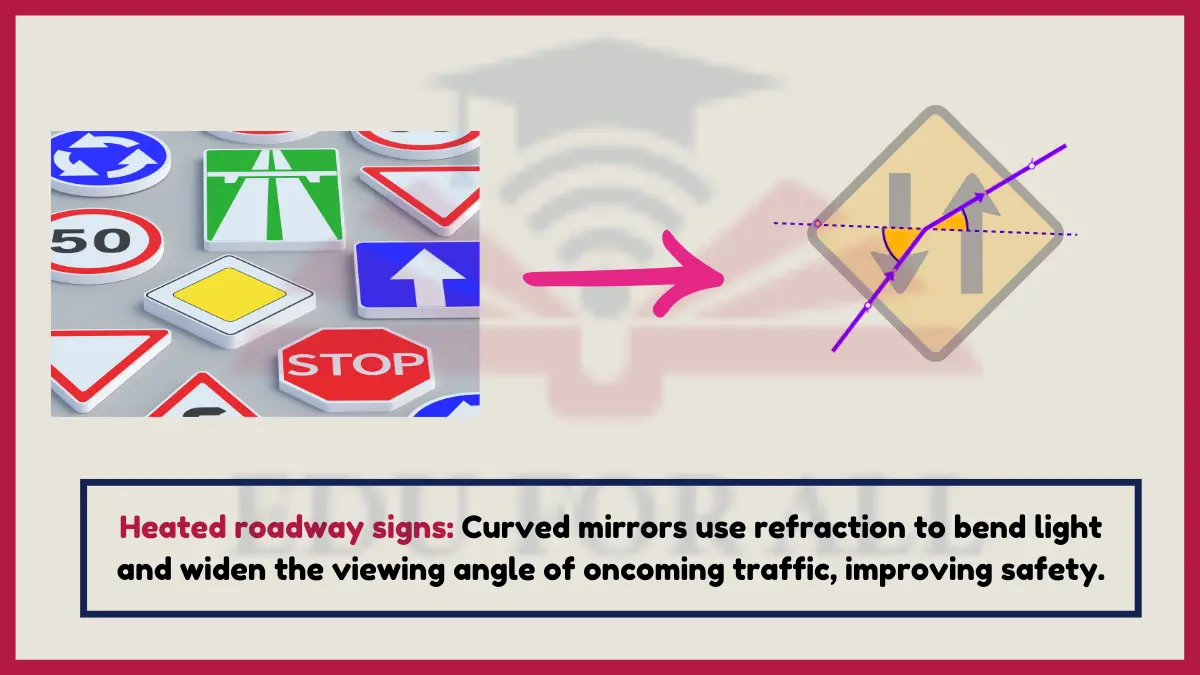
Their curvature and wide aspect ratio enables greatly expanded intersection sight coverage from existing poles versus limited head rotations alone.
Experiment: Study bulging crossing mirrors to consider expanded peripheral refractive vision augmentation improving driving insight.
20. Multicolored sports sunglasses
Specialized sports sunglasses with multiple colored filters are designed based on light refraction principles to enhance contrast for certain objects like tennis balls, making them stand out more sharply for improved performance.

Experiment: As an informal experiment, students can borrow or try on such eyewear and observe which colors seem intensified or diminished when looking around.
Also Read:

